Typically an Ethernet network interface is built-in to most modern motherboards. Some computer systems, especially server systems, are equipped with two network interfaces built-in to the motherboard. Additional interfaces can be installed in extra PCI expansion slots.
-

Typical Ethernet NIC PCI card
Try the command lspci -vv to see if the hardware is detected properly, and which kernel module (if any) is being assigned:
-
01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme BCM5764M Gigabit Ethernet PCIe (rev 10) Subsystem: Hewlett-Packard Company Device 1309 Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx+ Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx- Latency: 0, Cache Line Size: 64 bytes Interrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 52 Region 0: Memory at f7000000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=64K] Capabilities: <access denied> Kernel driver in use: tg3 Kernel modules: tg3 ... ... 37:09.0 Ethernet controller: Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme BCM5782 Gigabit Ethernet (rev 03) Subsystem: Hewlett-Packard Company Device 000c Physical Slot: 5 Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR+ FastB2B- DisINTx- Status: Cap+ 66MHz+ UDF- FastB2B+ ParErr- DEVSEL=medium >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx- Latency: 32 (16000ns min), Cache Line Size: 64 bytes Interrupt: pin A routed to IRQ 21 Region 0: Memory at f8000000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=64K] [virtual] Expansion ROM at f7100000 [disabled] [size=64K] Capabilities: <access denied> Kernel driver in use: tg3 Kernel modules: tg3
or more specifically lspci -vv | grep Ethernet
-
01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme BCM5764M Gigabit Ethernet PCIe (rev 10) 37:09.0 Ethernet controller: Broadcom Corporation NetXtreme BCM5782 Gigabit Ethernet (rev 03)
The network configuration tools and network configuration files are different for Ubuntu/Debian vs Red Hat/Fedora based systems.
The following commands will start, stop or restart networking:- sudo /etc/init.d/networking start
- sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop
- sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
Ubuntu GUI network configuration tool: /usr/bin/gnome-nettool (apt-get install gnome-nettool)
One can also configure Ubuntu systems by adding entries to the configuration file:
/etc/network/interfaces
-
Dynamic IP:
... ... auto eth1 iface eth1 inet dhcp
Static IP:... ... auto eth1 iface eth1 inet static address 192.168.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 network 192.168.1.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
Address and netmask are required. The system can calculate defaults for the other values.
DNS configuration will be required in /etc/resolv.conf. For this and other networking configurations see the YoLinux Networking tutorial.
The most simple method of configuring Red Hat based distributions is by using the console based GUI tool:
system-config-network
-



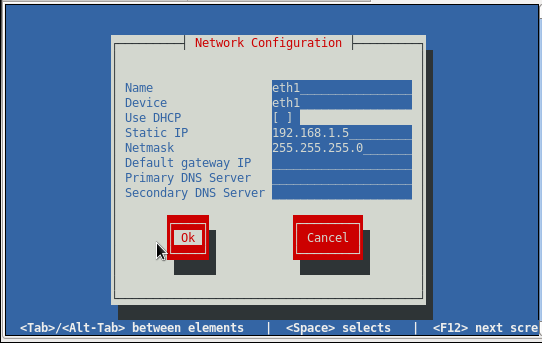
Both static and dynamic configurations can be set. If configuring for DHCP, go to that line and pres the space bar. An asterisk "*" will appear to show that this option has been selected.
After device configuration, the new device will show up in the list.
- /sbin/ip addr show
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether fa:ac:14:24:5e:8d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.12.2/24 brd 192.168.12.255 scope global dynamic eth0 valid_lft 77603sec preferred_lft 77603sec inet6 fe80::477:3e3e:d5fd:823a/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 3: eth1: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether fa:ac:14:24:5e:8f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff 4: wlan0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether 28:b2:bd:36:a7:3b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ffOR - /sbin/ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 64:31:50:24:41:A1 inet addr:242.27.32.60 Bcast:242.27.32.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 inet6 addr: fb80::6631:50ff:fb44:46a1/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:845 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:191 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:158077 (154.3 KiB) TX bytes:15619 (15.2 KiB) Interrupt:17 eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:17:24:BF:77 inet addr:192.168.1.5 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0 UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:0 (0.0 b) TX bytes:0 (0.0 b) Interrupt:21 lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:330704 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:330704 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:917208006 (874.7 MiB) TX bytes:917208006 (874.7 MiB)
The addition and configuration of the new Ethernet device will generate the new file:
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
-
DEVICE=eth1 BOOTPROTO=static NETMASK=255.255.255.0 TYPE=Ethernet HWADDR=00:10:17:24:bf:77 IPADDR=192.168.1.5
See /usr/share/doc/initscripts-*/sysconfig.txt for the explanation of all options.
The command ifup eth1 and ifdown eth1 are used to bring the new Ethernet interface card into service or offline.
DNS configuration will be required in /etc/resolv.conf. For this and other networking configurations see the YoLinux Networking tutorial.
- Linux Networking and Configuration - subnetting, routing, configuration, DNS, multiple IP's per NIC, etc
- Linux gateway routing - using forwarding and iptables
- Integrating with the Microsoft Network



 Books:
Books:
















